Types of relationships in Relational Databases
In this article I would like to present you all about relationships in relational databases. As you will learn from this article, there are not only basic relationships like One-To-Many or One-To-One. Maybe some of you use them unawares. It is good place to learn some new things about not obvious relationships. Let's start!
One-To-One | One-To-Many | Many-To-Many
These three are basic relationships, with which we can build more advanced ones. I already described them in one of my last articles. I invite you to familiarise with and to gain some knowledge from it. Apart from basic relations you can find more about basic concepts of relational databases. Click to enter my article!
Category Relationship
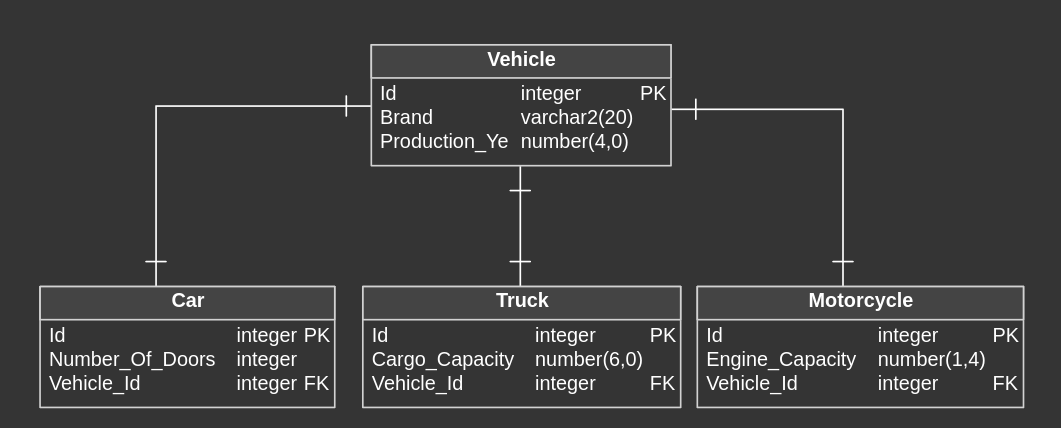
It is more one of more advanced category, which you may used unawares in your entity relationship diagrams or when you designed your database. Category relationship is specific case, which we can notice for example in situations, when entity can be the member of one of many categories, but these categories share common qualities.
In other words this relationship occurs, when one entity is highlighted as superior entity and other are child entities. Superior entity enables to inherit properties by other, child entities.
Example
Vehicles can be classified for example as a car, truck or motorcycle. Each vehicle has common qualities like brand, registration number or production year but some of their properties can be different. In this case Vehicle entity will be superior entity and Car, Truck, Motorcycle entities will be child entities. There is One-To-One relatioship between each of them.
Recurvise Relationship
It is case, when entity is related to itself. It means, that one record in the table can be related with other record in the same table. Recursive Relationships are commonly used in modeling of hierarchical structures such as family relationships, organizational trees or product structures.
Recursive Relationship can be:
- One-To-Many - Represented by foreign key from the same table.
- Many-To-Many - Represented by intermediate, additional table between two instances of the same table.
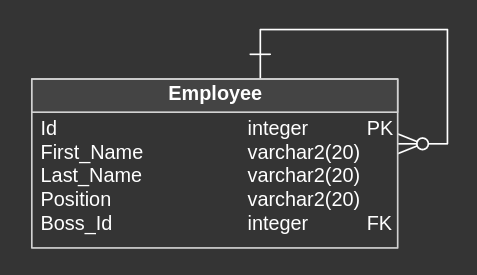
One-To-Many Recursive Relationship example
Each employee of some company is assigned to the boss, who is simultaneously employee of the same company. This relationship is created with usage of One-To-Many relationship, because one employee has one boss, but one boss can supervise multiple employees
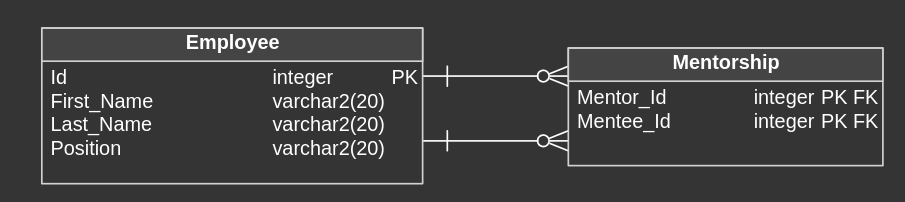
Many-To-Many Recursive Relationship example
Imagine scenario, where employees can mentor other employees, and each employee can be mentored by multiple employees. This relationship is created with additional table and One-To-Many relationships (to achieve Many-To-Many).
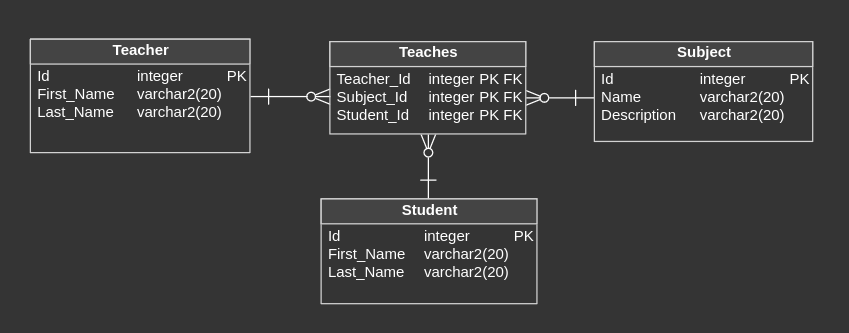
Ternary Relationship
It is situation, in which three different entities are related to each other in a single relationship. In the opposite to commonly used binary relationships (between two tables) here we need to combine three elements.
Example
We have three entities: Student, Subject and Teacher. Ternary Relationship would occur, when we would like to record, which teacher teaches a specific student a particular subject. To achieve it, we need to create additional table, which combine those three entities.
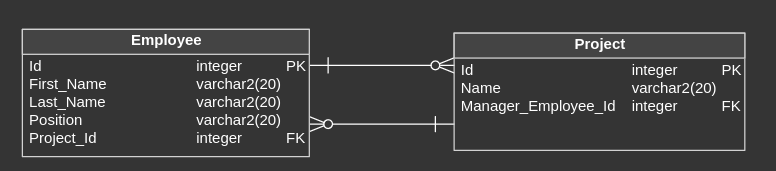
Cyclic Reference
It refers to situation, when two or more tables in our database have mutual reference. This approach often generate problems such as difficulties with maintaining data integrity or really complex SQL queries, but you can of course encounter this relationship in some databases.
Example
We have Employee and Project tables. In Employee table we store, among others, information about project, in which employee is participating. In Project table we can find Manager_Employee_Id column, which indicates, which employee is manager of the project.