How to improve your app efficiency with asynchronous methods and functions?

Recently, during Miesiany Miesiany Kebab application development I solved interesting problem related to app efficiency, which inspired me to create this article. I would like to share with you description of this case, my solution and the consequences from using this approach. On the end I will describe briefly, what exactly asynchronous means.
Problem
As I said before, I came across this problem while developing my application for gastronomic industry. More specifically, I created newletter with email verification and notifications about new promotions – some util classes and services responsible for notifying subscribers. Everything worked fine, emails were sent correctly and business logic was in line with expectations. There was one problem: poor performance. More specifically, each email was sent synchronously, which means, that the application had to wait for each email to be processed before proceeding the next one. This led to a situation where sending emails to a large number of subscribers significantly slowed down the system, causing large delays.
Solution
To solve this issue, I decided to try asynchronous programming. Backend of my application is built with usage of Spring and other related technologies, so all my work relied on enabling global async support (by adding @EnableAsync annotation in my main application class) and adding @Async annotation over appropriate methods definitions. You can see examples below.
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class KebabApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(KebabApplication.class, args);
}
}
@Async
public void sendEng(NewsletterSubscriber subscriber, Promotion promotion) throws MessagingException {
MimeMessage message = javaMailSender.createMimeMessage();
MimeMessageHelper mimeMessageHelper = new MimeMessageHelper(message, true, "UTF-8");
mimeMessageHelper.setTo(subscriber.getEmail());
mimeMessageHelper.setSubject(SUBJECT_ENG);
Context context = getPromotionContext(subscriber, promotion, NewsletterMessagesLanguage.ENGLISH);
String htmlContent = templateEngine.process("promotion-mail", context);
mimeMessageHelper.setText(htmlContent, true);
javaMailSender.send(message);
}
Consequences of this approach
🔴 Improved efficiency
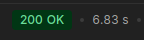
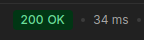
System no longer waits for each email to be sent before moving on to the next one. By making methods asynchronous I achieved 201x speed improvement! Look at the comparison below:
Synchronous approach. Sending email to 4 subscribers
Asynchronous approach. Sending email to 4 subscribers
Definition of asynchronous
In programming, asynchronous refers to the ability to execute many tasks independently and simultaneously. This allows tasks to be initialized and runned without waiting for the previous ones to finish. Instead of blocking the program until task is completed, asynchronous tasks run in the background and notify program once they are done.
This is the opposite of synchronous operations, where task must be completed before the next one starts. For this reason asynchronous approach is used in many cases like sending emails, downloading data or performing long-running calculations. If your app performance is poor, consider using asynchronous methods/functions where it makes sense.
Remember, that this approach is universal and independent of any programming language. It doesn’t matter in which language your app is created. Keep this approach in your mind for future!