How to combine data from multiple tables with SQL JOIN?

Storing data in multiple tables is distinguishing property of relational databases. To get desired data and information, we are often forced to refer to more than one table. We can actually do this with SQL JOINs or with WHERE clause, but the first approach is better and safer. We will focus on it in this article.
Attention! In this article I am describing JOINs, which are available in Oracle DBMS. Other systems also supports majority of these operations, but make sure, that this, which you would like to test is definitely supported by your database. For example FULL OUTER JOIN is not supported by MySQL. In this case you should try to combine two queries with UNION operator to achieve the same result.
Database Schema
To explain majority of JOIN types I would like to use this simple database schema, with the following tables and example data:
Clients
- id: 1 | first_name: Anna
- id: 2 | first_name: Marek
- id: 3 | first_name: Jan
Orders
- id: 1 | client_id: 1 | product | Laptop
- id: 2 | client_id: 3 | product | Printer
- id: 3 | client_id: NULL | product | Telephone
INNER JOIN
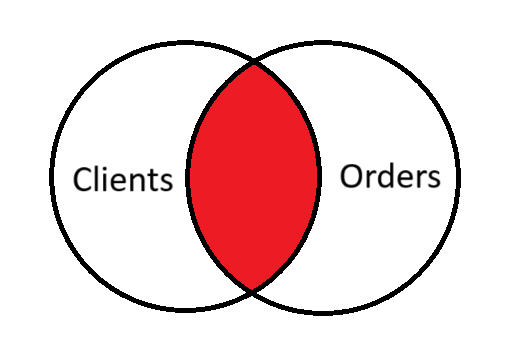
Returns only those rows, which have matching values in both tables. INNER keyword is optional in SQL query.
Example query
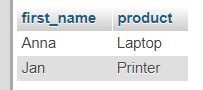
SELECT Clients.first_name, Orders.product
FROM Clients
INNER JOIN Orders ON Clients.id= Orders.client_id;
Result
LEFT (OUTER) JOIN
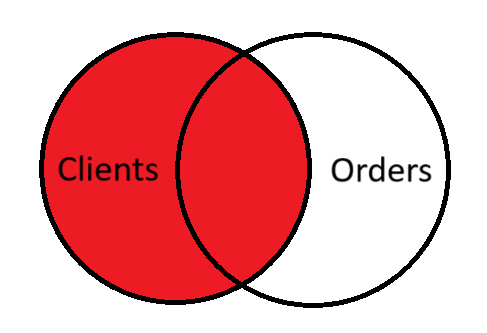
Returns all rows from the left table (this specified before LEFT JOIN cluses), even if there are no matching rows in the right table. When there is no match, the values in the right table are NULL. OUTER keyword in SQL query is optional.
Example query
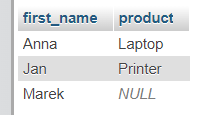
SELECT Clients.first_name, Orders.product
FROM Clients
LEFT JOIN Orders ON Clients.id = Orders.client_id;
Result
RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN
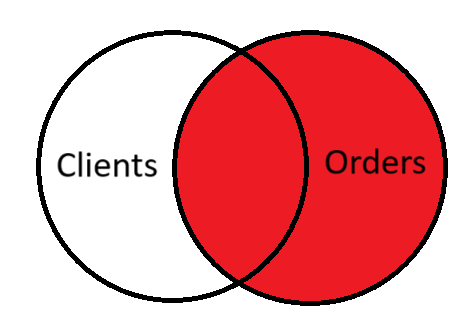
Works similarly to LEFT JOIN, but returns all rows from the right table (this specified after RIGHT JOIN keywords), even if there are no matching rows in the left table. OUTER keyword in SQL query is optional.
Example query
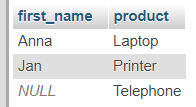
SELECT Clients.first_name, Orders.product
FROM Clients
RIGHT JOIN Orders ON Clients.id = Orders.client_id;
Result
FULL (OUTER) JOIN
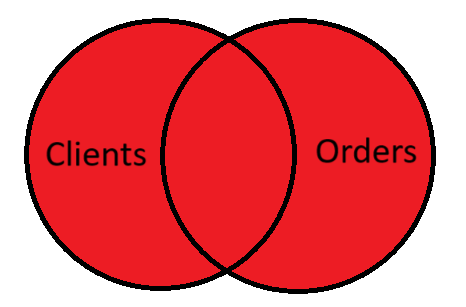
Returns all rows both from the left and right table. If there are no matching, rows will be fulfilled with NULL.
Example query
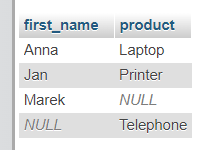
SELECT Clients.first_name, Orders.product
FROM Clients
FULL OUTER JOIN Orders ON Clients.id = Orders.client_id;
Result
CROSS JOIN
Returns cartesian product of two tables, which means, that each row from first table is combined with each row in second table.
Example query
SELECT Clients.first_name, Orders.product
FROM Clients
CROSS JOIN Orders;
Result
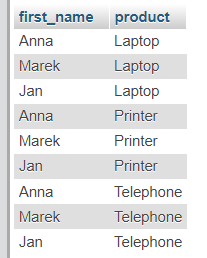
Result

Combining table with itself (Self-Join)
Imagine, that you have recursive relationship. Then you may need to join the table with itself. Self-join is useful when you need to compare rows within the same table or establish relationships between rows in the same dataset. To differentiate between the "copies" of the table, you use table aliases.
Database schema
Students
- id: 1 | name: Alice | mentor_id: NULL
- id: 2 | name: Bob | mentor_id: 1
- id: 3 | name: Charlie | mentor_id: 1
- id: 4 | name: David | mentor_id: 2
- id: 5| name: Emma | mentor_id: 3
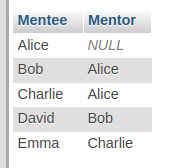
Example query
SELECT
mentee.name AS Mentee,
mentor.name AS Mentor
FROM Students mentee
LEFT JOIN Students mentor
ON mentee.mentor_id = mentor.id;
Result

Combining more than two tables
With JOINs we can of course combine more than two tables. Now I would like to show you how to do this, but firstly we should update our first database schema.
Database schema
Clients
- Without change.
Orders
- id: 1 | client_id: 1 | product_id: 2
- id: 2 | client_id: 3 | product_id: 1
- id: 3 | client_id: 2 | product_id: 3
Products
- id: 1 | product: Laptop | price: 5400
- id: 2 | product: Printer | price: 600
- id: 3 | product: Telephone | price: 2500
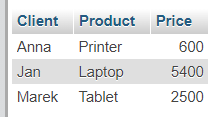
Example query with INNER JOIN
SELECT
Clients.first_name AS Client,
Products.product AS Product,
Products.price AS Price
FROM Clients
INNER JOIN Orders ON Clients.id = Orders.client_id
INNER JOIN Products ON Orders.product_id = Products.id;
Result
Venn diagram of the result
Joins based on parameters other than the foreign and primary keys
Not every join is a foreign key / primary key based. We can also join tables based on other properties, for example range of values (range of numbers, dates or others). This particular case is achievable with BETWEEN condition within ON clause. Database schema for this example:
Database schema
Employees
- id: 1 | name: John | salary: 5000
- id: 2 | name: Alice | salary: 7000
- id: 3 | name: Bob | salary: 10000
Salary_Ranges
- id: 1 | category: Low income | min_salary: 0 | max_salary: 6000
- id: 2 | category: Medium Income | min_salary: 6001 | max_salary: 8000
- id: 3 | category: High Income | min_salary: 8001 | max_salary: 12000
Example query
SELECT
Employees.name,
Salary_Ranges.category,
Employees.salary
FROM Employees
JOIN Salary_Ranges ON Employees.salary BETWEEN Salary_Ranges.min_salary AND Salary_Ranges.max_salary;
Result
